Water is the source of life and is crucial for the health and survival of all living organisms on Earth. However, due to various contaminants affecting surface water and groundwater, drinking water often contains issues such as residual chlorine, organic pollutants, and disinfection by-products. These substances not only affect the taste of drinking water but may also have adverse effects on human health.
As an efficient and economical water treatment technology, activated carbon performs excellently in the field of drinking water purification. By adsorbing and removing various pollutants from water, activated carbon can significantly improve the quality of drinking water, ensuring that people consume clean and hygienic water.
This article will focus on the application and advantages of activated carbon in drinking water treatment.
Sources and Hazards of Pollutants In Drinking Water

Drinking water contains many pollutants, mainly from the following sources:
- Microbial Contaminants: Such as bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and parasites, which can cause gastrointestinal diseases and other health problems.
- Heavy Metals: Such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and arsenic, which can damage the brain, nervous system, and kidneys.
- Pesticides and Herbicides: Chemicals used in agricultural activities that may enter water sources through surface runoff.
- Industrial Chemicals: Such as benzene, toluene, dichloromethane, and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs).
- Pharmaceutical Residues: Such as antibiotics and other drug components, which may come from medical waste or human excretion.
- Disinfection By-products: Such as trihalomethanes (THMs), which are formed during the water treatment process when disinfectants react with organic substances in the water.
- Algae and Their Toxins: Such as microcystins, which may be produced during water eutrophication.
- Organic Pollutants: Such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), dioxins, and furans.
These pollutants can lead to unpleasant taste and odor in drinking water and pose health risks. Therefore, using activated carbon to treat and purify drinking water is crucial.
Drinking Water Purification Process
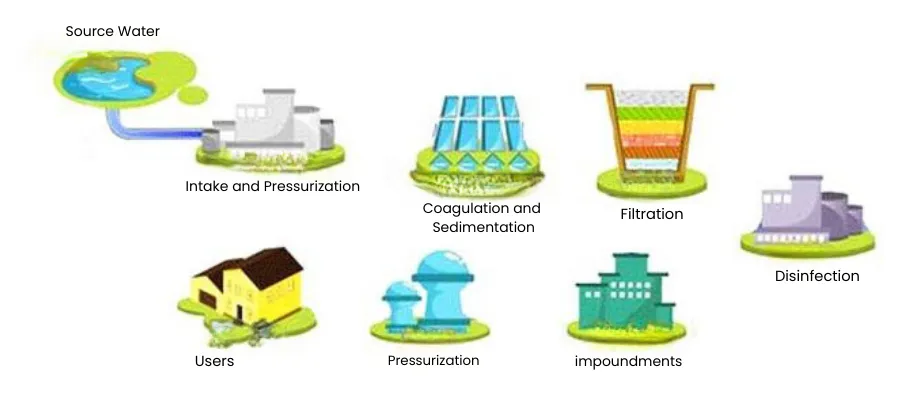
The goal of drinking water treatment is to ensure water safety, hygiene, and compliance with drinking standards. The following is a general process for drinking water treatment:
Pre-treatment
- Removal of Large Particles: Remove large particles such as sand and leaves from the water through screens or sedimentation tanks.
- pH Adjustment: Adjust the pH of the water by adding acids or bases to make it suitable for subsequent treatment steps.
- Removal of Residual Chlorine: Remove residual chlorine in the water by adding chemicals such as sodium bisulfite.
- Suspended Solids Filtration: Remove suspended solids in the water through coarse filtration.
Conventional Treatment
- Coagulation: Add coagulants to raw water to aggregate suspended solids and colloidal substances into larger flocs for easier separation.
- Sedimentation: Settle the large flocs formed after coagulation through sedimentation tanks to preliminarily clarify the water.
- Filtration: Remove fine particles, organic matter, bacteria, and viruses from the water using filtration tanks for further water purification.
- Disinfection: Add disinfectants such as chlorine or ozone to kill bacteria and viruses in the water, ensuring water safety.
Advanced Treatment
- Filtration: Further remove suspended solids and impurities from the water.
- Disinfection: Again kill bacteria and viruses in the water to ensure higher safety standards.
- Softening: Reduce water hardness through ion exchange or chemical softening methods to prevent scale formation.
- Deodorization: Remove unpleasant odors and harmful gases from the water through activated carbon adsorption, oxidation, or aeration.
Disinfection
Common disinfection methods include chlorine disinfection, ozone disinfection, and ultraviolet (UV) disinfection.
- Chlorine Disinfection: The most commonly used method, effectively kills bacteria and viruses in the water.
- Ozone Disinfection: Has strong oxidizing properties, effectively kills bacteria and viruses without residuals but is costly.
- UV Disinfection: Non-polluting and residue-free, effectively kills bacteria and viruses.
The Role of Activated Carbon in Drinking Water Purification

In the drinking water treatment process, activated carbon adsorption typically occurs in the advanced purification stage, following conventional coagulation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection steps.
At this stage, most suspended solids and microorganisms have been removed, and activated carbon acts as a highly efficient filter, specifically adsorbing residual trace organic pollutants, disinfection by-products, odor substances, etc. further enhancing water quality and ensuring the safety and taste of drinking water.
Activated carbon’s high adsorption efficiency is due to its well-developed pore structure and large specific surface area, much like a sponge filled with tiny pores, capable of capturing and securely holding tiny pollutant molecules in the water.
Moreover, the chemical functional groups on the surface of activated carbon can also react with certain pollutants, enhancing the adsorption effect.
Selection of Activated Carbon For Drinking Water Purification

Choosing the right activated carbon for drinking water treatment is crucial as it directly affects treatment efficiency and final water quality. Below are considerations for selecting activated carbon and specific product recommendations:
Activated Carbon Selection
Granular Activated Carbon is commonly used in drinking water treatment due to its high adsorption capacity and suitability for large-scale, continuous water treatment processes. Selection factors include:
- Raw Material: Commonly used materials include coal and coconut shell. Coal-based activated carbon is more economical.
- Specific Surface Area: Should generally exceed 900 m²/g; the larger the surface area, the stronger the adsorption capacity.
- Particle Size: Common sizes are 12×40 or 8×30 mesh; should be chosen according to specific water treatment facility requirements.
- Iodine Number: Reflects the extent of micropore development; typically required to be greater than 900 mg/g.
- Abrasion Resistance: Affects service life; generally required to be greater than 90%
Product Recommendations
Here are some high-performance activated carbon products suitable for drinking water treatment:
Calgon Carbon Filtrasorb 400
Granular activated carbon with high adsorption capacity, excellent mechanical strength, and regeneration performance. Suitable for removing organic pollutants and disinfection by-products, widely used in municipal water treatment plants.
Jacobi Aquasorb 2000
Granular activated carbon with high specific surface area and micropore structure. Specifically designed to remove volatile organic compounds and chlorine by-products from water. Offers excellent chemical stability and adsorption performance.
Tingyuan Carbon
Tingyuan is a company specializing in the research, production, sales, and service of activated carbon. Our granular activated carbon products have high specific surface area and well-developed pore structure, providing strong adsorption capacity to efficiently purify drinking water contaminants.
We have certifications such as NSF、KOSHER and HALAL, and our products meet health and safety standards. We are committed to meeting diverse customer needs, offering customizable products.
Get a competitive quoteAs a professional activated carbon supplier, Tingyuan Carbon is dedicated to providing high-quality products and professional technical support to customers. For further inquiries or more product information, please contact us.
- Whatsapp: +86-13323528218
- Email: info@tycarbon.com

